k8s operator 패턴 구현 (Operator Framework)
개요 :
Red Hat이 주도하는 오픈소스 프로젝트로, 오퍼레이터 개발을 단순화하고 자동화하기 위한 다양한 도구와 라이브러리를 제공합니다. Operator SDK는 Kubebuilder 기반으로 만들어졌지만, Helm, Ansible 등 다양한 언어와 프레임워크를 지원합니다. 또한 레드햇이 주도하여 개발 중으로 보이는 openstack operator 프로젝트에 사용되었습니다.
쿠버네티스의 오퍼레이터와 오퍼레이터 패턴은 공식 문서 https://kubernetes.io/ko/docs/concepts/extend-kubernetes/operator/에 정리되어 있습니다.
오퍼레이터(Operator)는 사용자 정의 리소스를 사용하여 애플리케이션 및 해당 컴포넌트를 관리하는 쿠버네티스의 소프트웨어 익스텐션이다. 오퍼레이터는 쿠버네티스 원칙, 특히 컨트롤 루프를 따른다.
쿠버네티스 코드 자체를 수정하지 않고 기능을 확대한다는 점에서 큰 이점을 가지고 있습니다. 이미 cncf 의 많은 프로젝트들이 해당 기법을 사용하여 기능을 제공하고 있습니다. CKA 시험에서도 24년 11월 25일 이후부터 시험항목에 관련 내용이 추가됩니다.
Operator Framework 는 크게 세 가지 특성 Operator SDK(build, test, iterate), Operator Lifecycle manager(install, manage, update), Operatorhub.io (Publish & share) 을 제공 합니다.
이번 글에서는 코드 수준의 오퍼레이터 코드 작성 및 빌드 방식에 집중합니다.
kubebuilder 구조
operator framework 가 내포한 kubebuilder는 아래와 같은 구조를 가지고 있습니다.
kubebuilder 는 controller-runtime 이 핵심 라이브러리 입니다. [ https://github.com/kubernetes/sample-controller/blob/master/controller.go 이런 예시 프로젝트가 code-generator 기반 인 것과 비교할 수 있습니다. ]
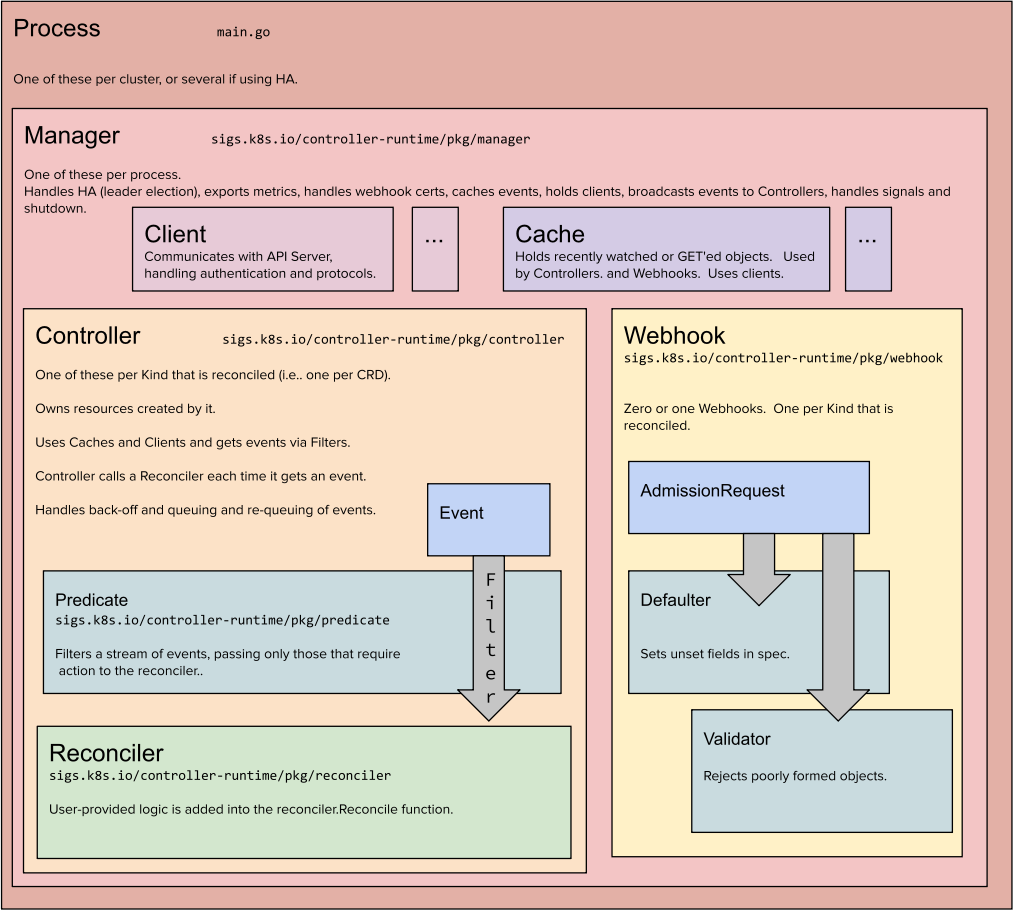
이미지에서 controller-runtime의 각 구성 요소(Client, Cache, Controller, Predicate, Reconciler, Webhook)에 대한 설명을 아래에 정리했습니다:
1. Client
위치: sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client
역할:
- Kubernetes API 서버와 통신하는 인터페이스로, API 요청을 전송합니다.
- 리소스를 조회(Create, Get, List), 수정(Update, Patch), 삭제(Delete)할 수 있는 메서드를 제공합니다.
- 캐시된 데이터를 조회할 수도 있으며, 필요한 경우 API 서버로 직접 요청을 보냅니다.
특징:
- 캐시된 데이터를 먼저 조회하여 성능을 최적화합니다.
- 인증 및 프로토콜 처리를 자동으로 수행합니다.
2. Cache
위치: sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/cache
역할:
- 최근 Watch 또는 GET 요청에서 조회된 리소스를 저장하는 메모리 내 캐시입니다.
- Informer를 사용하여 Kubernetes 리소스를 캐싱하고, 변경 사항을 지속적으로 업데이트합니다.
특징:
- Controller와 Webhook에서 공통적으로 사용됩니다.
- 캐시를 통해 API 서버와의 통신 횟수를 줄이고, 성능을 높입니다.
3. Controller
위치: sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/controller
역할:
- 리소스의 변경 사항을 감지하고, 이를 Reconciler에 전달하여 리소스 상태를 관리합니다.
- 각 CRD(Custom Resource Definition)마다 하나의 Controller가 생성됩니다.
특징:
- 이벤트 필터링(Filtering)을 통해 필요한 이벤트만 처리할 수 있습니다.
- 큐(Queue)를 사용하여 백오프(Backoff) 및 재시도(Re-queuing)를 관리합니다.
- Reconciler를 호출하여 상태를 조정하는 로직을 실행합니다.
4. Predicate
위치: sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/predicate
역할:
- 이벤트를 필터링하여 Reconciler에 전달할 필요가 있는지 여부를 결정합니다.
특징:
- Create, Update, Delete, Generic 이벤트에 대해 필터링 로직을 구현할 수 있습니다.
- 예를 들어, 특정 레이블이 있는 리소스의 변경 사항만 처리하거나, 특정 필드 값의 변경만 감지할 수 있습니다.
5. Reconciler
위치: sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/reconcile
역할:
- 리소스의 현재 상태와 원하는 상태를 비교하고, 이를 동기화하는 로직을 구현합니다.
- 사용자 정의 Reconciler는 Reconcile 메서드를 구현해야 합니다.
특징:
- Reconcile 메서드는 이벤트가 발생할 때마다 호출되며, 리소스를 업데이트하거나 다른 API 요청을 전송할 수 있습니다.
- 주로 idempotent(멱등성)을 유지하도록 설계되어야 합니다.
- Reconcile 메서드의 반환 값은 reconcile.Result로, 재시도 여부와 간격을 결정할 수 있습니다.
6. Webhook
위치: sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/webhook
역할:
리소스의 Admission Request(생성, 업데이트 요청)를 가로채어 검증 및 수정 작업을 수행합니다.
종류:
- Defaulter: 리소스의 기본값을 설정합니다. 필드 값이 비어 있을 경우 기본값을 채워 넣습니다.
- Validator: 리소스의 유효성을 검사합니다. 잘못된 형식이나 비정상적인 값이 있는 경우 요청을 거부합니다.
특징:
- Kubernetes API 서버와의 통신을 통해 AdmissionRequest를 처리합니다.
- 사용자 정의 Webhook을 통해 리소스 검증 및 수정 로직을 추가할 수 있습니다.
문서 따라하기
https://sdk.operatorframework.io/docs/building-operators/golang/tutorial/ 문서를 따라 합니다.
overview
- 다음 프로젝트를 수행합니다.
- Memcached 디플로이먼트가 존재하지 않는다면, 생성합니다.
- 커스텀 리소스 스펙에 정의된 isk 크기와 동일한 상황에 있는 것을 보장합니다.
- Memcached CR의 상태를 Status Writer를 통해 해당 CR의 파드 이름을 사용하여 업데이트 합니다.
설치
**Compile and install from master**
```bash
git clone https://github.com/operator-framework/operator-sdk
cd operator-sdk
git checkout master
make install
```
프로젝트 생성
mkdir memcached-operator
cd memcached-operator
operator-sdk init --domain example.com --repo github.com/example/memcached-operator
환경 확인
~/memcached-operator $ ls
cmd config Dockerfile go.mod go.sum hack Makefile PROJECT README.md test
--domain 은 API group의 prefix가 됩니다. k8s에서의 대표적 그룹 예시는 apps 나 rbac.authoriztion.k8s.io 가 있습니다. 좀 더 구체적인 내용(쿠버네티스의 api를 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다)은 https://book.kubebuilder.io/cronjob-tutorial/gvks.html 에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 또한 생성된 프로젝트의 기본 구조는 https://book.kubebuilder.io/cronjob-tutorial/basic-project.html 문서를 확인하면 좋습니다.
- go.mod
- Makefile : 프로젝트 작업에 필요한 여러 명령어들이 정리되어 있습니다. 해당 파일을 분석하면 어떤 작업을 할 수 있는지 대략적으로 감을 잡을 수 있습니다.
- PROJECT : Kubebuilder 가 사용할 메타데이터 입니다. 새로운 구성요소를 scaffolding (리소스를 빠르게 초기화하고 설정할 수 있는 템플릿이나 자동화된 생성 도구를 의미) 하는 데 필요 합니다.
config 폴더 아래에는 Kustomize YAML 정의들을 가지고 있고, 추후에 컨트롤러를 작성하기 시작하면, 커스텀 리소스 정의나 RBAC 설정 그리고 웹훅 설정 등도 생성되게 됩니다.
참고로 --repo=<path> 설정은 $GOPATH/src 밖에서 프로젝트를 생성할 때 사용 되어야 합니다.
Manager
cmd/main.go 는 오퍼레이터의 메인 프로그램이고 Manager를 초기화하고 구동 시킵니다.
매니저는 네임스페이스의 제한 둘 수 있습니다. 해당 네임스페이스에서만 모든 컨트롤러는 리소스를 watch 할 수 있습니다.
mgr, err := ctrl.NewManager(cfg, manager.Options{Namespace: namespace})
만약 모든 네임스페이스를 가능하게 하려면, 빈 값으로 두면 됩니다.
mgr, err := ctrl.NewManager(cfg, manager.Options{Namespace: ""})
Operator scope에 대한 더 심도있는 내용은 https://sdk.operatorframework.io/docs/building-operators/golang/operator-scope/ 문서를 살펴보아야 합니다.
Create a new API and Controller
~/memcached-operator $ operator-sdk create api --group cache --version v1alpha1 --kind Memcached --resource --controller INFO[0000] Writing kustomize manifests for you to edit... INFO[0000] Writing scaffold for you to edit... INFO[0000] api/v1alpha1/memcached_types.go INFO[0000] api/v1alpha1/groupversion_info.go INFO[0000] internal/controller/suite_test.go INFO[0000] internal/controller/memcached_controller.go INFO[0000] internal/controller/memcached_controller_test.go INFO[0000] Update dependencies: $ go mod tidy INFO[0000] Running make: $ make generate mkdir -p /home/syyang/memcached-operator/bin Downloading sigs.k8s.io/controller-tools/cmd/controller-gen@v0.15.0 go: downloading sigs.k8s.io/controller-tools v0.15.0 go: downloading k8s.io/api v0.30.0 go: downloading k8s.io/apiextensions-apiserver v0.30.0 go: downloading k8s.io/apimachinery v0.30.0 go: downloading golang.org/x/tools v0.20.0 go: downloading golang.org/x/sys v0.19.0 go: downloading golang.org/x/net v0.24.0 /home/syyang/memcached-operator/bin/controller-gen object:headerFile="hack/boilerplate.go.txt" paths="./..." Next: implement your new API and generate the manifests (e.g. CRDs,CRs) with: $ make manifests환경 확인
~/memcached-operator $ ls api cmd Dockerfile go.sum internal PROJECT test bin config go.mod hack Makefile README.mdapi/v1alpha1/memcached_types.go를 통해 api 리소스가 만들어지고controllers/memcached_controller.go를 통해 컨트롤러가 만들어집니다. (정확히는 scaffold 합니다)참고
더 완벽한 튜토리얼을 위해서는 아래 명령을 시도해볼 수 있습니다.
$ operator-sdk create api --group cache --version v1alpha1 --kind Memcached --plugins="deploy-image/v1-alpha" --image=memcached:1.4.36-alpine --image-container-command="memcached,-m=64,modern,-v" --run-as-user="1001"이번 예제는 single group API 경우에 대해서 다룹니다. multi-group 은 https://book.kubebuilder.io/migration/multi-group.html 문서를 확인해야 합니다.
controller-runtime에서 설정한 설계 목표를 제대로 따르기 위해, 프로젝트에서 생성된 각 API를 관리하는 전용 컨트롤러를 하나씩 두는 것이 권장됩니다.
Define the API
먼저, Memcached 타입을 정의하여 API를 표현할 것입니다. 이 타입은 MemcachedSpec.Size 필드를 통해 배포할 Memcached 인스턴스(CR)의 수를 설정하고, MemcachedStatus.Conditions 필드를 통해 CR의 상태(Conditions)를 저장할 것입니다.
api/v1alpha1/memcached_types.go 파일에서 Go 타입 정의를 수정하여 Memcached Custom Resource(CR)의 API에 다음과 같은 spec과 status를 추가하면 됩니다.
// MemcachedSpec defines the desired state of Memcached type MemcachedSpec struct { // INSERT ADDITIONAL SPEC FIELDS - desired state of cluster // Important: Run "make" to regenerate code after modifying this file // The following markers will use OpenAPI v3 schema to validate the value // More info: https://book.kubebuilder.io/reference/markers/crd-validation.html // +kubebuilder:validation:Minimum=1 // +kubebuilder:validation:Maximum=5 // +kubebuilder:validation:ExclusiveMaximum=false // Size defines the number of Memcached instances // +operator-sdk:csv:customresourcedefinitions:type=spec Size int32 `json:"size,omitempty"` // Port defines the port that will be used to init the container with the image // +operator-sdk:csv:customresourcedefinitions:type=spec ContainerPort int32 `json:"containerPort,omitempty"` } // MemcachedStatus defines the observed state of Memcached type MemcachedStatus struct { // Represents the observations of a Memcached's current state. // Memcached.status.conditions.type are: "Available", "Progressing", and "Degraded" // Memcached.status.conditions.status are one of True, False, Unknown. // Memcached.status.conditions.reason the value should be a CamelCase string and producers of specific // condition types may define expected values and meanings for this field, and whether the values // are considered a guaranteed API. // Memcached.status.conditions.Message is a human readable message indicating details about the transition. // For further information see: https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#typical-status-properties // Conditions store the status conditions of the Memcached instances // +operator-sdk:csv:customresourcedefinitions:type=status Conditions []metav1.Condition `json:"conditions,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"type" protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=conditions"` }CRD 매니페스트에 status 서브리소스를 추가하려면, +kubebuilder:subresource:status 마커를 사용해야 합니다.
// Memcached is the Schema for the memcacheds API //+kubebuilder:subresource:status type Memcached struct { metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"` metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"` Spec MemcachedSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"` Status MemcachedStatus `json:"status,omitempty"` }Spec은 사용자가 원하는 상태(desired state)를 정의합니다. Status 는 현재의 실제 상태(actual state)를 나타냅니다. 추가한 마커를 통해, 서브리소스를 추가하고, 이를 통해 컨트롤러는 CR 객체의 나머지 부분을 변경하지 않고, status 필드만 업데이트할 수 있습니다.
참고로
*_types.go파일을 수정한 후, 해당 리소스 타입의 생성된 코드를 업데이트하기 위해 항상make generate명령어를 수행해야 합니다. Makefile 타겟은controller-gen유틸리티를 호출하여api/v1alpha1/zz_generated.deepcopy.go파일을 업데이트합니다. 이를 통해 모든 Kind 타입이 구현해야 하는runtime.Object인터페이스를 우리의 API Go 타입 정의가 구현하도록 보장합니다.위의 설명을 좀 더 풀어서
zz_generated.deepcopy.go파일에 대해 설명하자면, Kubernetes는 컨트롤러, 캐시, 인덱서 등에서 객체를 복사하고 조작합니다. 이 과정에서 안전한 객체 복사(deepcopy)가 필수적입니다. DeepCopyObject() 함수는runtime.Object인터페이스를 구현합니다.type Object interface { GetObjectKind() schema.ObjectKind DeepCopyObject() Object }// DeepCopyObject is an autogenerated deepcopy function, copying the receiver, creating a new runtime.Object. func (in *Memcached) DeepCopyObject() runtime.Object { if c := in.DeepCopy(); c != nil { return c } return nil }이후
make manifests를 통해 CRD 매니페스트 파일을 생성할 수 있습니다.config/crd/bases/cache.example.com_memcacheds.yaml경로에 생성됩니다.Implement the Controller
internal/controllers/memcached_controller.go파일을 아래 내용으로 교체합니다.원 파일
/* Copyright 2024. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. */ package controller import ( "context" "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime" ctrl "sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime" "sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client" "sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/log" cachev1alpha1 "github.com/example/memcached-operator/api/v1alpha1" ) // MemcachedReconciler reconciles a Memcached object type MemcachedReconciler struct { client.Client Scheme *runtime.Scheme } // +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=cache.example.com,resources=memcacheds,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete // +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=cache.example.com,resources=memcacheds/status,verbs=get;update;patch // +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=cache.example.com,resources=memcacheds/finalizers,verbs=update // Reconcile is part of the main kubernetes reconciliation loop which aims to // move the current state of the cluster closer to the desired state. // TODO(user): Modify the Reconcile function to compare the state specified by // the Memcached object against the actual cluster state, and then // perform operations to make the cluster state reflect the state specified by // the user. // // For more details, check Reconcile and its Result here: // - https://pkg.go.dev/sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime@v0.18.4/pkg/reconcile func (r *MemcachedReconciler) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) { _ = log.FromContext(ctx) // TODO(user): your logic here return ctrl.Result{}, nil } // SetupWithManager sets up the controller with the Manager. func (r *MemcachedReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error { return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr). For(&cachev1alpha1.Memcached{}). Complete(r) }
이를 원래 파일과 비교하면 내용이 꽤나 많이 추가된 것을 볼 수 있는데, 아래의 내용은 컨트롤러가 어떻게 리소스를 감시하고 reconcile loop 이 작동하는 지 설명합니다.
Setup a Recorder
main.go 에
Recorder: mgr.GetEventRecorderFor("memcached-controller"),를 추가합니다.if err = (&controller.MemcachedReconciler{ Client: mgr.GetClient(), Scheme: mgr.GetScheme(), Recorder: mgr.GetEventRecorderFor("memcached-controller"), }).SetupWithManager(mgr); err != nil { setupLog.Error(err, "unable to create controller", "controller", "Memcached") os.Exit(1) }Reconciler의 개념은 다음과 같습니다. Reconciler는 Kubernetes에서 컨트롤러의 핵심 로직을 담당하는 구조체입니다. Kubernetes에서 컨트롤러는 목표 상태(desired state)와 현재 상태(actual state)를 비교하고, 이를 일치시키는 작업을 수행합니다. Reconciler는 이 과정에서 각 리소스(Custom Resource 포함)를 관찰하고, 필요한 업데이트나 변경 사항을 처리합니다. Event Recorder는 Kubernetes 리소스에서 발생하는 이벤트를 기록하는 역할을 합니다.
Resources watched by the Controller
controllers/memcached_controller.go파일의SetupWithManager()함수는 컨트롤러가 어떻게 구축되어, 해당 CR 및 컨트롤러가 소유하고 관리하는 다른 리소스들을 감시할지를 정의합니다.import ( ... appsv1 "k8s.io/api/apps/v1" ... ) func (r *MemcachedReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error { return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr). For(&cachev1alpha1.Memcached{}). Owns(&appsv1.Deployment{}). Complete(r) }NewControllerManagedBy()함수는 다양한 컨트롤러 구성을 가능하게 하는 컨트롤러 빌더를 제공합니다.For(&cachev1alpha1.Memcached{})는 Memcached 타입을 주요 감시 대상 리소스로 지정합니다. 각 Memcached 객체에 대해 Add/Update/Delete 이벤트가 발생할 때마다, 해당 Memcached 객체에 대한 reconcile 요청(네임스페이스/이름 키)이 Reconcile 루프로 전송됩니다.Owns(&appsv1.Deployment{})는 Deployment 타입을 보조 감시 대상 리소스로 지정합니다. 각 Deployment 객체에 대해 Add/Update/Delete 이벤트가 발생하면, 이벤트 핸들러는 이를 해당 Deployment의 소유자에 대한 reconcile 요청으로 매핑합니다. 이 경우, Deployment의 소유자는 해당 Memcached 객체입니다.이 경우, 의존 객체(Deployment)는
Owner References필드에 자신의 소유 객체를 참조해야 합니다. 이 필드는ctrl.SetControllerReference메서드를 사용하여 추가할 수 있습니다.참고: k8s API는
ownerRef필드에 따라 리소스를 관리합니다. 이 메서드를 사용하면ownerRef가 올바르게 설정됩니다. 따라서, K8s API는 Memcached Kind의 Custom Resource에 의존하는 리소스(예: Memcached Operand 이미지를 실행하는 Deployment)를 인식하게 됩니다. 이렇게 하면 Custom Resource가 삭제될 때, 모든 의존 리소스도 함께 삭제될 수 있습니다.Controller Configurations
이외에 컨트롤러를 시작하기 위한 여러 유용한 설정들이 존재합니다. 아래 내용 말고도 builder 와 controller godoc를 통해 다른 설정들을 더 자세하게 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
concurrent Reconciles 의 최대 수를 지정하는 옵션은 아래와 같습니다. (기본 값은 1 입니다)
func (r *MemcachedReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error { return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr). For(&cachev1alpha1.Memcached{}). Owns(&appsv1.Deployment{}). WithOptions(controller.Options{MaxConcurrentReconciles: 2}). Complete(r) }predicates 를 통해 watch events를 필터링 할 수 있습니다.
감시 이벤트가 Reconcile 루프로의 요청으로 어떻게 변환될지를 결정하려면 적절한 EventHandler 타입을 선택해야 합니다. 기본(primary) 리소스와 보조(secondary) 리소스 관계보다 더 복잡한 Operator 관계에서는,
EnqueueRequestsFromMapFunc핸들러를 사용하여 감시 이벤트를 임의의 Reconcile 요청 세트로 변환할 수 있습니다.
Reconcile 함수는 감시 중인 CR 또는 리소스에서 이벤트가 발생할 때마다 이 함수가 실행되며, 목표 상태와 현재 상태가 일치하는지 여부에 따라 반환값이 달라집니다.
이와 같이, 모든 컨트롤러는 Reconcile() 메서드를 구현하는 Reconciler 객체를 가지고 있으며, 이 메서드는 Reconcile 루프를 구현합니다. Reconcile 루프는 Request 인자를 전달받는데, 이 인자는 네임스페이스/이름 키로, 캐시에서 주요 리소스 객체인 Memcached를 조회하는 데 사용됩니다.
import ( ctrl "sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime" cachev1alpha1 "github.com/example/memcached-operator/api/v1alpha1" ... ) func (r *MemcachedReconciler) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) { // Lookup the Memcached instance for this reconcile request memcached := &cachev1alpha1.Memcached{} err := r.Get(ctx, req.NamespacedName, memcached) ... }Reconciler, Client, 그리고 리소스 이벤트와 상호작용하는 방법에 대한 자세한 안내는 Client API 문서를 참고 하시면 됩니다.
Reconciler에서 사용할 수 있는 반환 옵션 몇 가지는 다음과 같습니다. 더 자세한 것 내용은 Reconcile godoc을 참고하셔야 합니다.
오류가 있는 경우:
return ctrl.Result{}, err오류가 발생하면, ctrl.Result{}와 함께 오류를 반환합니다. 이 경우, Reconcile 함수는 오류를 처리하고 재시도할 수 있습니다.
오류 없이 재시도 요청:
return ctrl.Result{Requeue: true}, nil오류는 없지만, Reconcile 루프를 다시 실행하고 싶을 때 사용합니다. Requeue: true 옵션은 즉시 재시도를 요청합니다.
Reconcile 중지:
return ctrl.Result{}, nil리소스의 현재 상태가 목표 상태와 일치할 때 사용합니다. Reconcile 루프를 멈추고, 추가적인 재시도는 요청하지 않습니다.
X 시간 후에 다시 Reconcile:
return ctrl.Result{RequeueAfter: 5 * time.Minute}, nil일정 시간이 지난 후에 Reconcile을 다시 실행하고 싶을 때 사용합니다. 위의 예시에서는 5분 후에 재시도합니다.
Specify permissions and generate RBAC manifests
컨트롤러가 관리하는 리소스와 상호작용하기 위해서는 특정 ****RBAC 권한이 필요합니다. 이러한 권한은 다음과 같은 RBAC 마커(RBAC markers)를 통해 지정할 수 있습니다.
//+kubebuilder:rbac:groups=cache.example.com,resources=memcacheds,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete //+kubebuilder:rbac:groups=cache.example.com,resources=memcacheds/status,verbs=get;update;patch //+kubebuilder:rbac:groups=cache.example.com,resources=memcacheds/finalizers,verbs=update //+kubebuilder:rbac:groups=core,resources=events,verbs=create;patch //+kubebuilder:rbac:groups=apps,resources=deployments,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete //+kubebuilder:rbac:groups=core,resources=pods,verbs=get;list;watch func (r *MemcachedReconciler) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) { ... }make manifests명령을 통해ClusterRole매니페스트를config/rbac/role.yaml경로에 생성합니다.이후 문서 내용은 배포 과정을 설명하고 있습니다.